|
Information on AER SLR. Moldova
AER was in the past, a small resin-producer from Moldova. The company
is now "out of business", but most of the kits are still available
on the internet and eBay. During the time that AER was active, they
produced a line of resin kit vehicles which were not released by other
companies. Some of the kits were very exclusive and some have still
not been manufactured by other companies. (AER earlier produced a
line of plastic kits based on Zis trucks - which kits are later also
released by PST, Toga and other manufacturers).
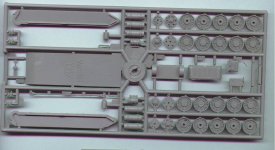
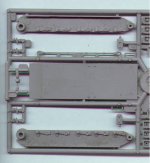
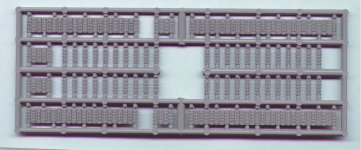
Kit Quality
AER's kits were not always of a high quality and/or very detailed.
The resin used is a strange mixture, hard as stone and easily broken
(like polyester mixed with plaster). Sanding is possible. The parts
are simply produced and need careful cleaning. Most of the time some
reworking of the details is required to bring the kit to a higher
detail level. Some of the kits have been modified and re-released.
These later versions are better detailed.
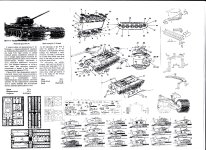
Instruction manual
The instruction manual is simple half A4 page and contains historical
vehicle info, drawings of the kit's parts and a simple schematic showing
"how to build up" the model.
Comments on Construction
Dry fitting is definitely required before any gluing is attempted.
Some filling may be needed in places.
Conclusions
These AER kits are definitely more for the advanced modellers with
some experience in scratch building. With some work it is possible
to build an acceptable kit. All of these kits are exclusive to AER
and, so far as I know, not available in plastic or resin by any other
manufacturers. In my opinion these AER kits are too high priced for
their quality.
Also, refer to Doug Chaltry's T-34
comparison article for additional information on the quality
of the AER T-34 kits.
_thn.jpg) |
Vehicle History
The “Komintern” artillery tractor was produced from
1934 until 1940. 1798 vehicles were produced. It was simple
and safe and could tow any gun of caliber up to 152mm and the
203mm howitzer B-4.
“Komintern” was one of the best of the medium tractors
of the 1930s. It took an active part in WWII and was used in
industry. 568 tractors were in use in the Soviet Army in 1945.
Losses from September 1942 till the end of the war were limited
to only 56 tractors.
Characteristics:
Years of manufacture – 1934 until 1940
Weight – 10.5 ton
Load-carrying capacity – 2 ton
Weight of towed trailer – 12 ton
Number of seats – 2 + 12
Engine power – 130 hp
Maximum speed 30 km
Range – 170 km
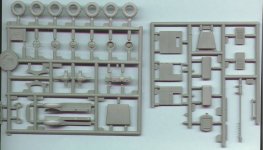
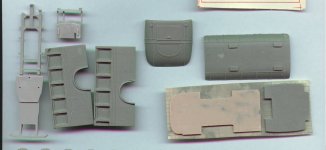
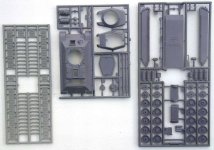
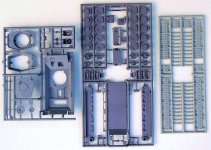
The box:
The kit is packed in a carton box with dimensions 22x15x3.5
cm. The kit parts are separately packed in plastic bags. All
parts are possibly in resin, but it is also possible that some
plastic parts from the AER Zis are included. No decals are included.
Quality of the kit:
If the plastic parts of the AER Zis-5 are included then there
is no problem
The resin parts are casted in a simple way and need to be cleaned
carefully. Most times it reworking some details is necessary
to bring the kit to a higher level of detailing.
Additional remark:
As far as I know, this vehicle is also released
by one or two other resin manufacturers. |
_thn.jpg) _thn.jpg) _thn.jpg)
_thn.jpg) _thn.jpg) _thn.jpg)
_thn.jpg) 
|
 |
Vehicle History
The Zis-16S Ambulance was produced in 1939-1944 and was a conversion
of the Zis-16 passenger bus. It had a simplified cabin adapted
from the Zis-5 lorry and the streamlined body of the base Zis-16
bus. The inside of the body was modified to transport a large
number of wounded men. Air ventilators and heating were included.
Zis-16S was used throughout WWII.
Technical Data:
Weight - 5,000kg
Seats - 20
Maximum speed - 65 km/hr
Length - 8,525mm
Width - 2,400mm
Height - 2,800mm
Engine - 85hp |






|
 |
Vehicle History
This Egyptian SPG (Self-propelled Gun) 122mm was created by joining
the hull of the Soviet tank T-34 with a Soviet D-30 Howitzer.
The howitzer was enclosed in a large turret which could be traversed
a full 360 degrees. Egypt used this SPG during the fighting with
Israel in 1974. |





|
_thn.jpg) |
Vehicle History
It was necessary to create a heavy tractor with a tank
engine to tow high power field guns (calibre 152-305mm guns),
as well as medium and heavy tanks which appeared in the Red
Army in the 1930s. Development of the tractor started in 1935
at the Komintern Steamlocomotive building plant in Kharkov.
In 1937 the development vehicle made a race to Moscow (and back),
where it was demonstrated in the Kremlin. The machine made a
strong impression and was approved. The tractor demonstrated
high results: it towed the largest artillery systems and all
types of tanks, including the T-35, very well. It could cross
fords up to 1.3 meter, and ditches up to 1.5 meter. It withstood
an uninterrupted all-day march without top-up.
Late in 1939 the manufacturing of the "Voroshilovets"
started. By September 1941, when the plant was evacuated to
Nizhni Taghil, 1123 vehicles were built. During the war the
tractor was efficiently used at all fronts for heavy transport
works, but most of all in the high power artillery units where
they had no equals – no army in the world had such a powerful
machine. Even the Germans respectfully called the small number
of captured tractors of this model “Stalin-607(R)”.
“Voroshilovets” stood all tests of war and came
to Berlin with the Red Army, and later took part in the Victory
Parade.
Technical Charateristics:
Weight: - 15 ton
Carrying capacity on platform – 3 ton
Weight of towed trailer - op to 20 ton
Max. Engine power – 375hp
Maximum Speed – 36 km
Fuel distance – 270 km
Length – 6218mm
Width – 2350mm
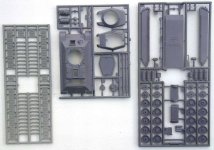
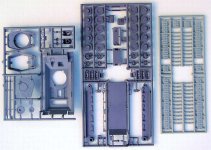
The box:
The kit is packed in a carton box with the following dimensions:
22x15x3.5 cm. The kit parts are separately packed in plastic
bags. All parts are in resin. Decals are included.
Quality of the kit:
The resin parts are casted in a simple way and need to be cleaned
carefully. Most times it reworking some details is necessary
to bring the kit to a higher level of detailing.
Additional remark:
As far as I know this vehicle was also released in resin by
two other manufacturers.
|
_thn.jpg) _thn.jpg) _thn.jpg) _thn.jpg)
.jpg) _thn.jpg)
_thn.jpg) _thn.jpg) _thn.jpg)
_thn.jpg) 
|
_thn.jpg) |
Vehicle History
This self propelled gun was used in the Red Army for
supporting mechanized units. It basically was an automobile
with a platform, on which was mounted a pedestal with a pivoting
regimental gun of 76.2mm, model 1927, containing an angular
shield.
The best-known model was a motorgun on the bassis of the Gaz
AAA model. It was sometimes also mounted on the three-wheeled
JAG-10 chassis.
In 1941 this model of the gun was produced in Leningrad in the
Kirov factory, mounted on the chassis of the Zis-5.
This gun could shoot both from secret and direct fire positions.
Its horizontal traverse was 270 degrees. Being widely used,
this self propelled gun proved to be sufficient to be considered
an effective mobile platform.
The box:
The kit is packed in a carton box with the following dimensions:
22x15x3.5 cm. The kit parts are separately packed in plastic
bags. All parts are possibly in resin, but it is also possible
that the plastic parts from the AER Zis-5 are included. No decals
are included.
Quality of the kit:
If the plastic parts of the AER Zis-5 are included then there
is no problem
The resin parts are casted in a simple way and need to be cleaned
carefully. Most times it reworking some details is necessary
to bring the kit to a higher level of detailing.
Additional information:
The Gaz AAA version is also available by UM (kit 322). |
|
 |
Vehicle History
At the beginning of the WWII, under the guidance of P.M. Muchalev
at the Kuibishev Military College, a mine-roller was developed
for the T-34 tank. It consisted in set of 4 steel disks which
rotated freely on axles, and attached in pairs to the frontal
plate of tank. The mine-roller was reliable, compact, and light
and was adopted by the Red Army with the designation of PT-34.
In June 1943, the Soviet Army formed the first regiment with mine-roller
tanks, which received its baptism of fire during the battles for
the Dnieper and the liberation of Kiev. The PT-34 mine roller
was also with the KV-1 tank.
Technical Data:
Mass - 5.3 ton
Width of rollers - 1.2 m
Speed - 10-18km/hr
|



|
 |
For some reason AER gave this
kit the same product number (7227) as their AER Zis-5 with short
76mm gun - 1941.
Vehicle History
The first Soviet self propelled gun was designed with the T-70
light tank as its basis. Starting in the autumn of 1942, through
to the end of WWII, some 13,932 Su-76s were manufactured. The
SPG used a Zis-3 gun which had the ability to pierce armor of
94mm thickness at 500m distance. The Su-76 was employed widely
during WWII as a tank hunter as well serving as an effective tool
for infantry support.
Technical Data:
Gun - 76mm Zis-3
Weight - 11.2 tons
Speed - 45 km/hr
Crew - 4 |






|
 |
Vehicle History
The Sau-100 SPG was created using the Soviet 100mm BS-3 gun mounted
in a new turret on a Soviet T-34 hull. This SPG actively used
in the Arab-Israeli conflict of 1967.
Technical Data:
Range of shot - 20 km
Initial shell velocity - 900m/sec
Armor penetration at 500m - 160mm
|








|
 |
Vehicle History
Gun:
In 1939 designer G.D. Dorokhin designed a new anti-aircraft gun,
using the barrel of an 85mm gun on the carriage of the 76mm AA
gun model 1938. During the WWII this gun was successfully used
by the air defence units. Over Moscow, 267 German planes were
shot down. Starting in 1942 the gun was successfully used in the
anti-armour role for the destruction of tanks where the armor-piercing
shells pierced armor all types of German tanks.
Weight of gun in fighting position - 4,300-4,900kg
Maximum Range- vertical - 10,500m, horizotal - 15,500m
Maximum Elevation- +82 degrees
Traverse - 360 degrees
Rapidity of fire - 20 shots/minute
Tractor:
It was necessary to create a heavy tractor with a tank engine
for towing high power field guns (calibre 152-305mm guns) as well
as medium and heavy tanks, which started to appear in the Red
Army during the 1930's. Development of the tractor started in
1935 at the Komintern Steamlocomotive building plant in Kharkov.
In 1937 the prototype made a trip to Moscow, and back, where it
was demonstrated at the Kremlin. The machine made a strong impression
and was approved for production. The tractor demonstrated good
performance,able to tow the largest artillery guns and all types
of tanks, including the T-35, very well. It was able to ford up
to 1.3 meters, travers ditches up to 1.5 meter, and was able to
run a full day without refueling. Late in the 1939 the manufacturing
of the "Voroshilovets" started. By September 1941, at which time
the plant was evacuated to Nizhni Taghil, some 1,123 vehicles
were built. During the war the tractor was effecively used on
all fronts for heavy transport duties, but mostly for the towing
of large calibre artillery where it had no equal - no other army
in the world had such a powerful machine. The Germans re-designated
the small number of captured tractors of this type as the Stalin
607(R). The "Voroshilovets" withstood all the tests of war and
entered Berlin with the Red Army, where it later took part in
the Victory Parade.
Technical Data:
Weight: - 15 tons
Load limit- 3 tons
Maximum weight of towed trailer - up to 20 tons
Max. Engine power - 375hp
Maximum Speed - 36 km/hr
Fuel Range - 270 km
Length - 6,218mm
Width - 2,350mm |









| |
_thn.jpg)
|
Vehicle History
In 1943 the Soviet arms industry
started designing the artillery tractor for replacement of
the "Voroshilovetz”. The first batch of new tractors
was assembled at the Kharkov tractor factory (KhTF) in September
1944. These tractors underwent successful military testing,
towing large calibre artillery systems, as well as medium
and heavy tanks.
Soon production of the AT-45 tractors was stopped, as KhTF
started to make the new T-44 tank.
The AT-45 is based on the T34 chassis.
Specifications:
Engine Capacity: - 350 hp
Weight: - 19 tons
Body capacity: - 35 persons
Bearing capacity: - 6 tons
Weight of a towed cargo - up to 25 tons
| |
|
| |
|

_thn.jpg)
_thn.jpg)
_thn.jpg)
_thn.jpg)
_thn.jpg)
_thn.jpg)
_thn.jpg)
_thn.jpg)


















_thn.jpg)
_thn.jpg)
_thn.jpg)
_thn.jpg)
_thn.jpg)
.jpg)
_thn.jpg)
_thn.jpg)
_thn.jpg)
_thn.jpg)
_thn.jpg)

_thn.jpg)
_thn.jpg)
_thn.jpg)
_thn.jpg)
_thn.jpg)
_thn.jpg)






































_thn.jpg)
.jpg)
_thn.jpg)
_thn.jpg)
_thn.jpg)
_thn.jpg)
_thn.jpg)
